Skin Discoloration or Texture Changes
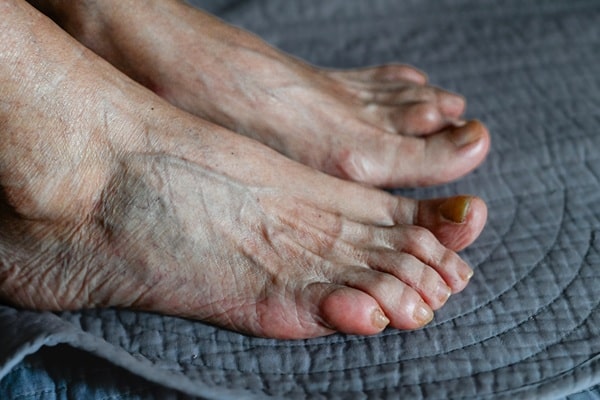
Changes in skin tone or texture can offer early clues about circulatory health. A purplish or bluish tint, especially in the toes or feet, signals that oxygen is not reaching the area properly. Shiny, thin, or unusually dry skin may also result from a lack of nutrients in the bloodstream. These signs may seem cosmetic, but they are often rooted in vascular issues.
Poor blood flow can deprive the skin of what it needs to maintain a healthy appearance and function. Over time, this can lead to cracking, sores, or slow-healing wounds, especially in people with diabetes. If skin changes appear alongside other symptoms, it becomes even more important to consult a healthcare provider. Addressing circulation problems early can help protect the skin and prevent long-term damage.
Numbness or Tingling Sensations
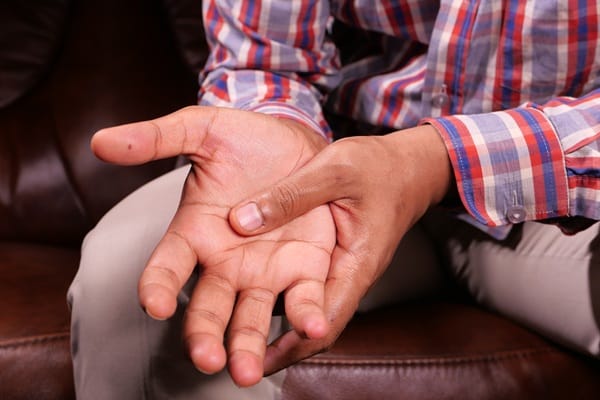
Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet often points to disrupted circulation and is not something to dismiss lightly. This symptom occurs when nerves do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients from the blood. Many people experience it as a “pins and needles” feeling that may come and go. While this may seem like a simple annoyance, frequent episodes suggest a larger issue.
Reduced circulation affects how well nerves can function and communicate with the brain. Conditions such as diabetes or narrowed blood vessels are common causes. Without enough blood flow, nerve tissues can become damaged over time, leading to permanent numbness or weakness. Recognizing this symptom as a sign of poor circulation can help prevent more serious neurological issues.
Muscle Cramps and Pain When Walking

Experiencing muscle cramps or leg pain during physical activity can be a subtle but serious warning of poor circulation. This discomfort often shows up after walking short distances and fades with rest, which can cause people to overlook it. The muscles in your legs require a steady supply of oxygen-rich blood, especially during movement. When circulation is reduced, the muscles are deprived of oxygen, leading to cramping, fatigue, or a burning sensation.
This condition is known as claudication and is commonly linked to peripheral artery disease. Many assume that the pain is a result of aging or poor fitness, but its repetitive nature reveals a deeper issue. If left untreated, the underlying vascular problem may worsen and limit mobility over time. Seeking evaluation early allows for interventions that can improve circulation and restore comfort during activity.